Funding for Solar Farms in Australia
Bloggerbanyumas.com – Australia’s renewable energy future hinges on the expansion of solar power. The country is already a global leader in solar energy adoption, with vast untapped potential to further harness the power of the sun. As we approach 2025, solar farms are positioned to play a critical role in helping Australia meet its ambitious renewable energy targets. However, scaling up solar farm projects requires substantial investment, effective funding strategies, and a robust support framework. This article provides a detailed analysis of funding opportunities for solar farms in Australia in 2025, covering government initiatives, private sector investments, and innovative financing models.

The Growing Importance of Solar Farms in Australia
Australia’s solar energy landscape is evolving rapidly, with solar farms becoming a major contributor to the national grid. The country enjoys one of the highest solar energy potentials globally, thanks to its vast and sunny landscape. As a result, solar farms in Australia are expected to meet an increasing share of the nation’s electricity demand, significantly reducing the reliance on fossil fuels and lowering carbon emissions.
By 2025, solar farms are projected to make up a significant portion of Australia’s renewable energy capacity. As of recent years, the Australian government has set an ambitious target of reaching net-zero emissions by 2050, with interim renewable energy goals driving further investments in solar infrastructure. This transition not only supports environmental sustainability but also creates a multitude of economic opportunities, including job creation, regional development, and energy security.
However, the development of solar farms requires significant upfront capital. Funding for solar farm projects is essential to ensure the continued growth of Australia’s solar capacity and meet its clean energy goals. This article will explore the various funding avenues available to solar farm developers and investors in 2025.
Understanding Solar Farm Financing in Australia
Funding for solar farms involves various financial mechanisms and stakeholders, from government incentives to private sector investments and innovative funding models. The development of a solar farm is a capital-intensive process that involves land acquisition, infrastructure development, panel installation, and grid connection. As a result, securing the right funding is essential for project success.
Key Factors Affecting Solar Farm Financing
Several factors influence the funding of solar farms in Australia. Understanding these key considerations is crucial for developers and investors looking to capitalize on the opportunities in the solar energy sector.
Capital Intensity of Solar Farms
Building a solar farm involves significant upfront capital expenditure. These costs include the purchase and installation of photovoltaic (PV) panels, inverters, transformers, and other necessary equipment. Additionally, costs for land acquisition, site preparation, and grid connection can be substantial. The capital-intensive nature of solar farm development means that projects often require funding over long periods, typically 10-25 years, before generating a return on investment.
Return on Investment (ROI)
The financial attractiveness of solar farms lies in their long-term, stable returns. Once operational, solar farms generate consistent cash flow through the sale of electricity. Solar power is a low-maintenance energy source, meaning operational costs are relatively low compared to conventional power plants. For investors, the steady cash flow from energy sales can provide a reliable ROI, making solar farms an appealing investment in Australia’s growing renewable energy sector.
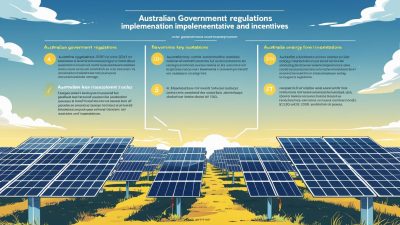
Regulatory Environment and Incentives
Government policies and incentives play a crucial role in financing solar farms. Australia’s renewable energy industry benefits from a supportive regulatory environment, including incentives such as the Renewable Energy Target (RET) and various tax benefits. These policies reduce financial risks for investors and encourage continued development of solar infrastructure. Understanding the regulatory landscape and the available incentives is essential for developers when securing financing for solar projects.
Types of Funding for Solar Farms in Australia
In Australia, the funding landscape for solar farms is diverse, encompassing a range of financing options, including government support, private investment, and innovative financing models. These funding avenues enable developers to secure the necessary capital to build, operate, and expand solar farms.
1. Government Grants and Subsidies
The Australian government provides several grants and subsidies to support the development of renewable energy projects, including solar farms. These incentives are designed to reduce the upfront costs of solar farm projects and stimulate private investment in clean energy infrastructure.
Renewable Energy Target (RET) Scheme
The Renewable Energy Target (RET) scheme, administered by the Australian Government, mandates that a certain percentage of Australia’s electricity be generated from renewable sources. The RET is designed to encourage investment in renewable energy projects, including solar farms. By 2025, the RET will continue to incentivize solar energy production, offering subsidies and credits to developers. The scheme allows solar farm owners to sell Renewable Energy Certificates (RECs), which can be traded to earn additional income. This revenue stream can significantly reduce the overall cost of solar farm development.
Clean Energy Finance Corporation (CEFC)
The Clean Energy Finance Corporation (CEFC) is a government-backed institution that provides funding for renewable energy projects, including solar farms. The CEFC’s primary goal is to facilitate the transition to a low-carbon economy by investing in clean energy technologies. It offers low-interest loans and equity funding for solar farm developers, with a focus on high-impact, large-scale projects. By 2025, the CEFC is expected to continue playing a pivotal role in supporting solar farm financing, particularly for developers who are looking to implement cutting-edge technologies and scale their operations.
Australian Renewable Energy Agency (ARENA)
The Australian Renewable Energy Agency (ARENA) is another government entity that supports the growth of solar energy in Australia. ARENA provides grants and funding for innovative renewable energy projects, including solar farm developments. Through its funding programs, ARENA helps reduce financial risks for developers and accelerates the deployment of renewable energy infrastructure. By 2025, ARENA is expected to continue to offer funding opportunities for solar farm projects that incorporate innovative technologies or improve the efficiency of solar energy generation.
2. Private Sector Investment
Private investment plays a vital role in financing solar farm projects in Australia. Solar farms require large capital commitments, and private investors, including institutional investors, energy companies, and venture capital firms, provide the necessary funding to bring these projects to life. There are several mechanisms through which private capital can be raised for solar farm development.
Equity Financing
Equity financing involves raising capital by selling ownership shares in the solar farm project to private investors. This model allows developers to secure the upfront capital needed for construction and other initial costs. Investors receive a return on their investment through dividends and capital gains as the solar farm generates revenue. Equity financing is particularly popular for large-scale solar farm projects, where substantial capital is required.
Debt Financing
Debt financing is another common method used to fund solar farms. In this case, developers borrow capital from banks or other financial institutions, which is then repaid over time with interest. Solar farm developers often use project financing, a type of debt financing that is secured against the future cash flows of the solar farm. This means that the loan is repaid using the revenue generated by selling electricity to the grid. Debt financing is typically used in conjunction with equity financing to ensure a balanced capital structure for solar projects.
Green Bonds and Solar Investment Funds
Green bonds are a form of debt financing specifically designed for environmentally sustainable projects, such as solar farms. These bonds are issued by developers or governments to raise capital for renewable energy projects, and the proceeds are exclusively used to finance green projects. Solar developers can issue green bonds to attract investors who are looking to support renewable energy projects.
Additionally, solar investment funds provide another avenue for financing solar farm projects. These funds pool capital from multiple investors and direct it toward solar farm development. By investing in solar funds, investors can diversify their portfolios while supporting the growth of solar energy.
3. Innovative Financing Models
In recent years, innovative financing models have emerged to provide alternative sources of funding for solar farm projects. These models are designed to address some of the challenges faced by traditional funding mechanisms, such as high upfront costs and lengthy payback periods.
Crowdfunding
Crowdfunding has gained traction in the renewable energy sector as a way to democratize investment in solar projects. Solar farm developers can raise small amounts of capital from a large number of individual investors through online platforms. Crowdfunding provides a way for retail investors to participate in solar energy projects, offering the potential for strong financial returns while contributing to the growth of renewable energy.
Power Purchase Agreements (PPAs)
A Power Purchase Agreement (PPA) is a contract between a solar farm developer and a purchaser (usually an energy retailer or large-scale energy consumer). Under a PPA, the developer agrees to sell the electricity generated by the solar farm at an agreed-upon price for a specified period, typically 10-20 years. PPAs provide a stable revenue stream for solar farm developers, making it easier to secure financing from lenders and investors.
Corporate Power Purchase Agreements (CPPAs)
Corporate Power Purchase Agreements (CPPAs) are similar to traditional PPAs, but they are specifically designed for corporations looking to purchase large amounts of renewable energy directly from solar farms. This model has gained popularity in Australia as more businesses commit to sustainability and carbon neutrality. Corporations enter into CPPAs to secure long-term, cost-effective renewable energy supply while helping solar farm developers secure financing.
The Future of Solar Farm Financing in Australia
As Australia moves towards its renewable energy targets, financing solar farm projects will continue to evolve. Government support, private sector investment, and innovative funding models will play key roles in ensuring the growth of solar energy in the country. By 2025, solar farm financing is expected to become more accessible, with new funding opportunities emerging as the demand for clean energy intensifies.
The ongoing support of Australian policymakers, combined with private sector investment and innovative financing structures, will be instrumental in meeting the country’s renewable energy goals. Solar farms will continue to be a driving force behind Australia’s energy transition, providing economic, environmental, and social benefits for years to come.
Conclusion
Funding solar farms in Australia in 2025 presents both opportunities and challenges for developers and investors. With a combination of government incentives, private sector funding, and innovative financing models, the solar industry is poised for significant growth. As the nation strives to meet its renewable energy targets, solar farms will be a cornerstone of Australia’s clean energy future, driving economic development, creating jobs, and contributing to a sustainable, low-carbon economy. Understanding the available funding options and choosing the right strategy is key to ensuring the continued expansion of solar energy in Australia.